k8s学习笔记-3(Pod yaml文件编写)
原创文档编写不易,未经许可请勿转载。文档中有疑问的可以邮件联系我。 邮箱:[email protected]
描述
Pod在k8s中归属apiVersion版本为v1。在编写yaml文件中apiVersion应该设置为v1。kind才能设置成Pod。
编写Pod的yaml文件时可以参考 kubectl explain --api-version=v1 pod. 一级一级查看具体的配置项。
apiVersion和kind对应关系参考:https://kubernetes.io/zh-cn/docs/reference/kubernetes-api/workload-resources/。
在通过yaml文件创建Pod时最好通过kubectl run 命令导出一个yaml文件。
本文对于Pod常用yaml配置进行演示,主要有勾子进程、健康性检查、初始化容器、Pod节点选择、node污点及容忍性。
模板文件导出命令: kubectl run test_name_pod --image=nginx --image-pull-policy=IfNotPresent --restart=Always --namespace=kube-system --labels=aa=12 --dry-run=client -o yaml > temp_pod.yaml
一、Pod生命周期勾子
勾子程序用在在pod开启关闭时通知应用级联操作,用在容器开启关闭前对容器进行自定义的命令或http端口拉取访问。
勾子程序有两个hook,一个为PostStart、PreStop,如果PreStop或者PostStart失败的话, 容器会停止。
- PostStart:在容器运行前执行操作,会阻塞Pod进入run的状态,如果PostStart hook未执行成功,Pod将无法进行running状态。
- PreStop:应用在容器停止前,会阻塞容器删除,但是过了terminationGracePeriodSeconds时间后,容器会被强制删除。
配置参考:kubectl explain pod.spec.containers.lifecycle
1.1 exec实例文件
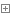

apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: creationTimestamp: null labels: run: test1-pod name: test1-pod spec: containers: - image: nginx imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent name: test1-pod resources: {} lifecycle: postStart: exec: command: ["/bin/bash", "-c", "touch /root/22"] preStop: exec: command: - cat - /root/22 dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst restartPolicy: Always status: {}
1.2 httpGet实例文件


apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: creationTimestamp: null labels: run: test2-pod name: test2-pod spec: containers: - image: nginx imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent name: test2-pod resources: {} lifecycle: postStart: httpGet: host: 10.244.190.70 path: / port: 80 scheme: HTTP dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst restartPolicy: Always status: {}
部分参数详解:
- host: 需要请求的主机地址
- path: web网页的路径
- port:对端web服务的端口
- scheme:连接主机的协议,默认HTTP
二、健康性检查
每个容器都会执行一个进程此进程由CMD和ENTRYPOINT指定,如果进程退出时返回码非零,则表示该容器发生故障,k8s会根据yaml文件中定义的restrtPolicy规则决定是否重启容器。
有时进程未退出则不会反会值,但是程序处于异常状态,此时需要额外的检测手段对容器进行检查,使用Liveness探测来确定容器中运行的程序能够提供正常的服务。
在容器启动完成过后但是容器中的应用不一定启动完成,对于对外服务的容器,需要使用Readiness决定容器什么时候可以加入到service中。
LIveness配置参考:kubectl explain pod.spec.containers.livenessProbe
Readiness配置参考:kubectl explain pod.spec.containers.readinessProbe
2.1 Liveness探测
Liveness探测让用户可以自定义判断容器是否健康,如果探测失败则重启容器。
2.1.1 exec实例文件
自定参数进行检测。

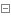
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: creationTimestamp: null labels: run: test3-pod name: test3-pod spec: containers: - image: nginx imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent name: test3-pod resources: {} lifecycle: postStart: exec: command: - sleep - "20" livenessProbe: exec: command: - cat - /root/22 periodSeconds: 11 initialDelaySeconds: 10 failureThreshold: 5 successThreshold: 1 timeoutSeconds: 3 dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst restartPolicy: Always status: {}
部分参数详解:
- periodSeconds: 每隔多少秒检测一次,默认10秒,最小值1秒。
- initialDelaySeconds: 容器启动过后多少秒开始检测,默认0秒。
- failureThreshold: 检测失败多少次确定程序异常,默认3次,最小1次。
- successThreshold: 检测成功多少次确定程序正常,必须为1,默认为1。
- timeoutSeconds: 检测超时时间默认1秒。
2.1.2 httpGet实例文件
用作http网页服务检测

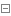
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: creationTimestamp: null labels: run: test4-pod name: test4-pod spec: containers: - image: nginx imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent name: test4-pod resources: {} lifecycle: postStart: exec: command: - sleep - "20" livenessProbe: httpGet: host: 10.244.190.70 path: / port: 80 scheme: HTTP periodSeconds: 11 initialDelaySeconds: 10 failureThreshold: 5 successThreshold: 1 timeoutSeconds: 3 dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst restartPolicy: Always status: {}
部分参数解释:
- host: 需要请求的主机地址
- path: web网页的路径
- port:对端web服务的端口
- scheme:连接主机的协议,默认HTTP
2.1.3 tcpSocket实例文件
用作tcp端口检测。

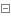
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: creationTimestamp: null labels: run: test5-pod name: test5-pod spec: containers: - image: nginx imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent name: test5-pod resources: {} lifecycle: postStart: exec: command: - sleep - "20" livenessProbe: tcpSocket: host: 10.244.190.70 port: 80 periodSeconds: 11 initialDelaySeconds: 10 failureThreshold: 5 successThreshold: 1 timeoutSeconds: 3 dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst restartPolicy: Always status: {}
部分参数解释:
- host: 需要请求的主机地址
- port:对端监听的TCP端口号
2.2 Readiness探测
Readiness可以检测容器什么时候满足对外提供服务的能力,即什么时候可以加入到service负载池中。Readiness探测语法和Liveness语法完全一致。
2.2.1 exec实例文件
自定义参数检查。
cat pod-readinessProve.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: creationTimestamp: null labels: run: test8-pod name: test8-pod spec: containers: - image: nginx imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent name: test8-pod resources: {} lifecycle: postStart: exec: command: - sleep - "20" readinessProbe: exec: command: - cat - /root/22 periodSeconds: 11 initialDelaySeconds: 10 failureThreshold: 5 successThreshold: 1 timeoutSeconds: 3 dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst restartPolicy: Always status: {}
部分参数详解:
- periodSeconds: 每隔多少秒检测一次,默认10秒,最小值1秒。
- initialDelaySeconds: 容器启动过后多少秒开始检测,默认0秒。
- failureThreshold: 检测失败多少次确定程序异常,默认3次,最小1次。
- successThreshold: 检测成功多少次确定程序正常,必须为1,默认为1。
- timeoutSeconds: 检测超时时间默认1秒。
2.2.2 httpGet实例文件
用作http网页服务检测。

apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: creationTimestamp: null labels: run: test6-pod name: test6-pod spec: containers: - image: nginx imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent name: test6-pod resources: {} lifecycle: postStart: exec: command: - sleep - "20" readinessProbe: httpGet: host: 10.244.190.70 path: / port: 80 scheme: HTTP periodSeconds: 11 initialDelaySeconds: 10 failureThreshold: 5 successThreshold: 1 timeoutSeconds: 3 dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst restartPolicy: Always status: {}
部分参数解释:
- host: 需要请求的主机地址
- path: web网页的路径
- port:对端web服务的端口
- scheme:连接主机的协议,默认HTTP
2.2.3 tcpSocket实例文件
用作tcp端口检测。

apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: creationTimestamp: null labels: run: test7-pod name: test7-pod spec: containers: - image: nginx imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent name: test7-pod resources: {} lifecycle: postStart: exec: command: - sleep - "20" readinessProbe: tcpSocket: host: 10.244.190.70 port: 80 periodSeconds: 11 initialDelaySeconds: 10 failureThreshold: 5 successThreshold: 1 timeoutSeconds: 3 dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst restartPolicy: Always status: {}
部分参数解释:
- host: 需要请求的主机地址
- port:对端监听的TCP端口号
二、初始化容器
在k8s中对于一些容器,在运行时必须满足一定的条件,但是又不能直接在容器中执行命令使环境到达满足容器运行的要求,因为在容器中执行命令可能会导致镜像里面的CMD和ENTRYPOINT指定命令发生改变从而导致容器运行不起来。
为了当前环境能够满足正式容器运行的条件,创建一个初始化容器对环境进行一个设置,待初始化容器对环境设置完成过后再运行主程序容器。
如果为一个 Pod 指定了多个 Init 容器,Init容器会按顺序一次运行一个。 每个 Init 容器必须运行成功才能够运行一个Init容器,所有Init容器运行完成才能运行Pod中的主程序容器。
Pod中所有容器的名称必须唯一包含Init容器和主程序容器,如果同一个Pod中有容器名称不唯一则会报错。
初始化容器一般用来对宿主机节点的配置进行修改。
配置参考:kubectl explain pod.spec.initContainers
2.1 使用Init预处理数据卷
创建两个卷datadir、datadir2。datadir使用指定宿主机中/data_pod为路径,datadir2随机在宿主机上生成一个文件夹作为存储数据路径。在初始化容器中挂在datadir卷,并在卷中创建一个文件,最后在主程序容器中挂在datadir卷。
emptyDir对于容器来说是持久卷,对于Pod来说不是持久卷,该方式创建的卷会跟随Pod删除而删除。
hostPath:对于Pod来说是持久卷,不会随着Pod删除而删除。
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: creationTimestamp: null labels: run: test9-pod name: test9-pod spec: volumes: - name: datadir hostPath: path: /data_pod - name: datadir2 emptyDir: {} initContainers: - name: init-container-01 image: busybox command: - touch - /pod_data/lvan.sh volumeMounts: - name: datadir mountPath: "/pod_data" containers: - image: nginx imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent env: - name: aa value: "456" - name: bb value: "test_env" name: test9-pod volumeMounts: - mountPath: "/data01" name: datadir - mountPath: "/data/02" name: datadir2 dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst restartPolicy: Always status: {}
2.2 使用Init修改宿主机配置
使用初始化容器对宿主机进行配置更改时首先需要共享需要更改的宿主机的文件夹到初始化容器中,对于宿主机内核相关信息更改,还需在创建容器时使用特权模式创建。
设置了特权模式的容器,可以对主机进行很多操作,比如,要修改宿主机内核参数等。

apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: creationTimestamp: null labels: run: test10-pod name: test10-pod spec: initContainers: - name: init-container-01 image: busybox command: - touch - /root/lvan.sh securityContext: privileged: true containers: - image: nginx imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent env: - name: aa value: "456" - name: bb value: "test_env" name: test10-pod dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst restartPolicy: Always status: {}
部分参数详解:
- privileged: 设置容器为特权模式,true
三、pod调度
创建Pod时可以指定Pod运行的worknode节点,直接指定运行的worknode将不受worknode上的污点影响。
3.1 nodeName
直接指定Pod运行在哪个宿主机上。

apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: creationTimestamp: null labels: run: test11-pod name: test11-pod spec: nodeName: node01.lvan containers: - image: nginx imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent env: - name: aa value: "456" - name: bb value: "test_env" name: test11-pod dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst restartPolicy: Always status: {}
3.2 nodeSelector
nodeSelector通过标签来确定Pod运行在哪个宿主机中。
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: creationTimestamp: null labels: run: test12-pod name: test12-pod spec: nodeSelector: kubernetes.io/hostname: node02.lvan containers: - image: nginx imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent env: - name: aa value: "456" - name: bb value: "test_env" name: test12-pod dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst restartPolicy: Always status: {}
四、node污点设置
没有污点的worknode可以支持可容忍污点的Pod。如果worknode上污点,那么表示不允许pod调度到该节点,除非pod也被标记为可以容忍污点节点。
可以使用污点来区分不同节点的类型,如环境中worknode节点物理配置不一样,有的磁盘比较好、有的网络比较好。可以添加污点却分出每种不同类型的nodework。
使用kubectl taint命令可完成Node节点污点设置。
设置了污点的Node,会根据设置的策略对Pod进行调度,可以让新的Pod不调度到该节点,也可以把现有节点的上Pod驱逐出该Node。
污点由标签和作用两部分组成,格式为: key=value:effect,其中key=value即为污点标签,部分,effect为该污点的具体作用。污点有三个effect动作。
effect策略解释:
- PreferNoSchedule:NoSchedule软策略,尽量不要调度到该节点上,如果环境中除了该节点外其他节点均不满足Pod运行,则会调度到该策略的workNode上。
- NoSchedule:设置Pod不调度到该workNode上,Pod设置了可以容忍该污点除外。
- NoExecute:设置workNode不能调度Pod,同时驱逐掉该workNode上已有的Pod。
4.1 节点污点查看
使用命令查看node下有哪些污点。
# kubectl describe node node_name | grep -iA1 Taints
如果结果为<none>表示没有设置污点。
4.2 节点污点设置
格式:key=value:effect
4.2.1 设置污点
# kubectl taint nodes node_name 标签名=标签值:NoSchedule # #设置节点node01.lvan污点标签为storage=low-storage,尽量不调度Pod到该节点。 # kubectl taint nodes node01.lvan storage=low-storage:PreferNoSchedule
4.2.2 去除污点
# kubectl taint node node_name 标签名=标签值:PreferNoSchedule-
# kubectl taint node node_name 标签名=标签值-
# kubectl taint node node_name 标签名- # #去除node01.lvan节点上storage:PreferNoSchedule污点 # kubectl taint node node01.lvan storage:PreferNoSchedule-
五、Pod容忍性
当节点设置了污点,同时污点的策略还是NoSchedule,Pod则不会调度到该节点上。如果需要在该workNode上运行Pod,则需要设置Pod能够对该节点的上的污点进行容忍。
yaml文件中污点设置参考:kubectl explain --api-version=v1 pod.spec.tolerations.
operator参数解释:
- Exists:节点上存在该标签的污点就行,不用在乎具体的值和动作。都可以容忍。
- Equal:节点上存在的污点标签值要和yaml文件中定义一致,动作可以省略才可以容忍。
5.1 Exists
节点上只要有yaml文件中对应标签名的污点即表示该Pod可容忍对应的污点。
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: creationTimestamp: null labels: run: test12-pod name: test12-pod spec: tolerations: - key: storage operator: Exists containers: - image: nginx imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent env: - name: aa value: "456" - name: bb value: "test_env" name: test12-pod dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst restartPolicy: Always status: {}
5.2 Equal
需要yaml中定义的容忍污点标签、值、动作和节点上的污点一致才可容忍节点上的污点。


apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: creationTimestamp: null labels: run: test12-pod name: test12-pod spec: tolerations: - key: storage operator: Equal value: low-storage effect: NoSchedule containers: - image: nginx imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent env: - name: aa value: "456" - name: bb value: "test_env" name: test12-pod dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst restartPolicy: Always status: {}
六、亲和性
k8s中亲和性分为节点亲和性和Pod亲和性两种。
- 节点亲和性:设置Pod和node的关系。
- Pod亲和性:设置Pod和Pod之间的关系。
节点亲和性和Pod亲和性有软亲和性和硬亲和性两种。
- 软亲和性:preferred打头的为软亲和性
- 硬亲和性:required打头的为硬亲和性。
配置参考kubectl explain pod.spec.affinity.
6.1 键值运算关系
持续更新2023年8月7日。